
The United States' liquefied natural gas (LNG) industry is at risk of losing out in the growing Chinese market, as the trade war between the two countries continues to escalate, analysts said.
The U.S. and China respectively announced on Aug. 7 and 8 another round of tariffs this time amounting to 25 percent on 16 billion U.S. dollars’ worth of imports from each country. The new tariffs, set to go into effect at the same time on Aug. 23, are coming on the heels of the previous ones that were mutually enacted on July 6 and that have affected 34 billion U.S. dollars’ worth of products.
In China's list of additional tariffs, LNG was included, which was a surprise to many, as the country is seeing an increasing demand for energy. China's demand for cleaner power will become the world's largest LNG importer by the 2019, according to data from the International Energy Agency(IEA).
Last year, the country bought 38 million tons of LNG from overseas and its total LNG consumption rose by 17 percent in just the first half of this year.
Data from China Customs shows that around five percent of China's imported LNG comes from the U.S. But that accounted for 15 percent of total U.S. exports -- a big share for U.S. producers. However, their market share in China may be significantly cut as the tariffs will largely increase the cost for Chinese importers.
"LNG is a pretty expensive type of energy resource, compared to coal and fuel-based oil. With all the tariffs, the cost of U.S. LNG for Chinese importers may be 30 percent higher than that of LNG from Australia and other countries," said Cao Yin, the founder of the Digital Renaissance Foundation.
There are reports saying that China has already curtailed its LNG imports from the U.S. That could hardly have been what President Donald Trump wanted when he spoke of building energy dominance for the U.S.
Chen Jiahe, the chief strategist of Cinda Securities, also pointed out that the potential for China's LNG imports is expected to only increase as the country has been working hard to reduce environmental pollution. Losing such a vast growing market for LNG consumption would not be a good idea for U.S. exporters.
Over 90 percent of China's LNG imports comes from five major suppliers: Australia, Qatar, Indonesia, Malaysia and Papua New Guinea. The International Energy Agency estimates China's demand for natural gas will increase by 60 percent from 2017 to 2023 to a total of 376 billion cubic meters.
Sources:cctvplus
Please Contact Us at:
admin@xindemarine.com


 Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar 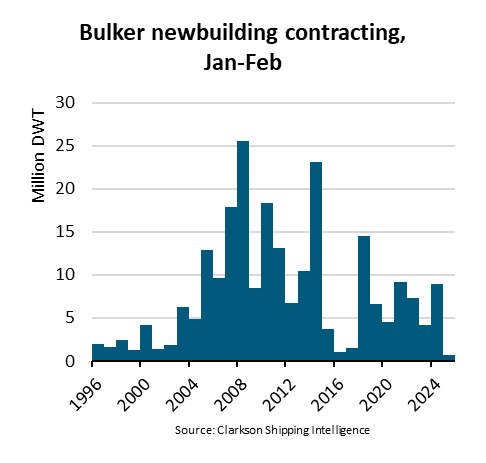 BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi
BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar